How to operate a drone is a question increasingly asked as these versatile machines become more accessible. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, covering everything from pre-flight checks and basic controls to advanced maneuvers and legal considerations. We’ll explore various drone types, their unique characteristics, and the safety protocols essential for responsible operation. Whether you’re a novice pilot or seeking to enhance your existing skills, this comprehensive resource will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to navigate the skies safely and effectively.
From understanding the nuances of multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones to mastering advanced techniques like waypoint navigation and cinematic shot composition, we aim to provide a practical and engaging learning experience. We’ll also address crucial legal and regulatory aspects, ensuring you operate within the bounds of the law and contribute to a safe airspace for all.
Drone Types and Their Operation
Understanding the different types of drones and their unique operational characteristics is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explore multirotor, fixed-wing, and single-rotor drones, detailing their operational differences, pre-flight checks, control inputs, and performance capabilities.
Multirotor Drone Operation
Multirotor drones, commonly known as quadcopters or octocopters, are characterized by their multiple rotors providing vertical lift and maneuverability. Their operation is relatively straightforward, making them popular for recreational and commercial use.
- Pre-flight Checks: Inspect rotors for damage, ensure battery is fully charged and securely connected, check GPS signal strength, and calibrate the compass.
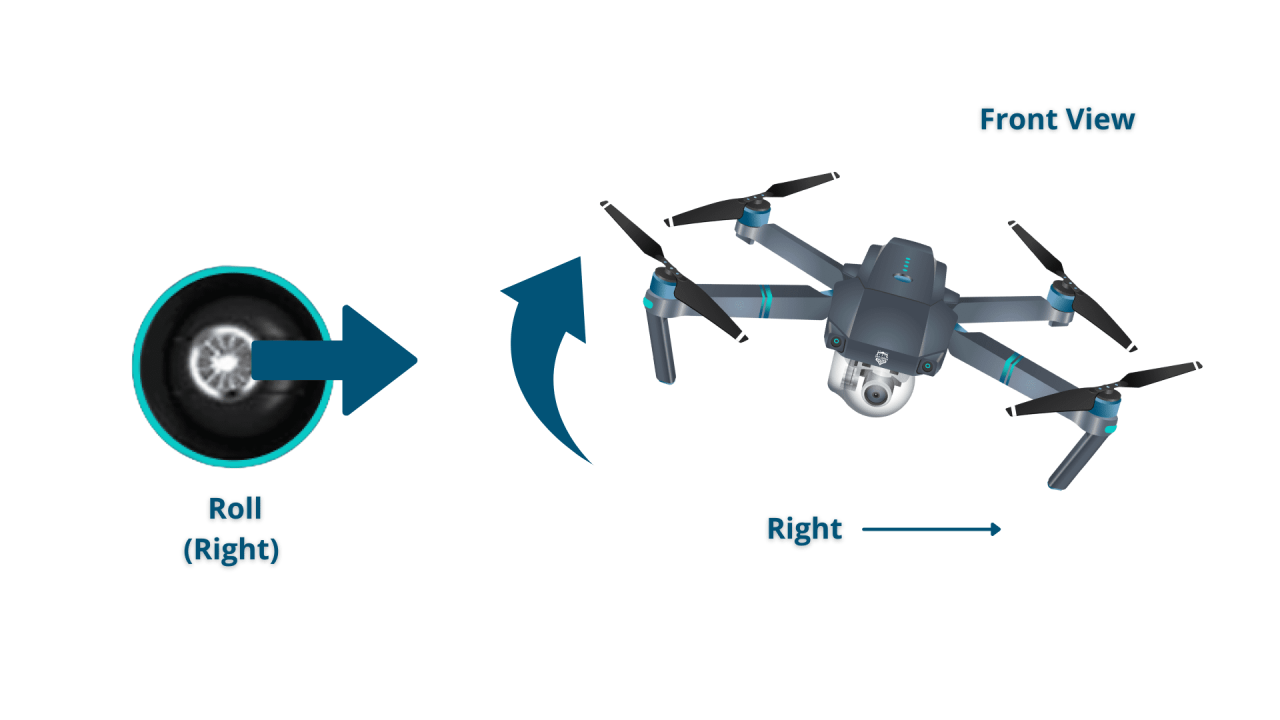
- Control Inputs: Two joysticks control altitude and movement. One controls pitch and roll (forward/backward, left/right), the other controls yaw (rotation) and throttle (ascent/descent).
- Unique Responses: Multirotors are highly maneuverable, capable of hovering and precise movements in all directions. They are susceptible to wind gusts, especially smaller models.
Fixed-Wing Drone Operation
Fixed-wing drones, resembling miniature airplanes, rely on forward momentum for lift. Their operation is more complex, requiring a greater understanding of aerodynamics and flight principles.
- Pre-flight Checks: Check propeller and wing integrity, ensure battery is securely mounted, verify GPS signal, and confirm pre-programmed flight path (if applicable).
- Control Inputs: Control inputs are similar to those of a traditional airplane, with controls for throttle, ailerons (roll), elevator (pitch), and rudder (yaw).
- Unique Responses: Fixed-wing drones are less maneuverable than multirotors, but they offer longer flight times and greater range. They require a runway for takeoff and landing.
Single-Rotor Drone Operation
Single-rotor drones, or helicopters, use a single rotor for lift and maneuverability. Their operation demands precision and skill due to their complex flight dynamics.
- Pre-flight Checks: Inspect the main rotor and tail rotor for damage, ensure the battery is securely connected and charged, check the gyroscope and accelerometer calibration, and verify GPS signal.
- Control Inputs: Typically involve cyclic (controls pitch and roll), collective (controls altitude), and anti-torque (controls yaw) controls.
- Unique Responses: Single-rotor drones offer exceptional maneuverability and the ability to hover precisely, but they are more challenging to operate than multirotors.
Drone Type Comparison
| Drone Type | Maneuverability | Flight Time | Payload Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multirotor | High | Moderate (15-30 minutes typically) | Moderate |
| Fixed-Wing | Moderate | High (30-60 minutes or more) | High |
| Single-Rotor | High | Moderate (20-40 minutes typically) | Moderate |
Pre-Flight Procedures and Safety
Prioritizing safety is paramount when operating a drone. Thorough pre-flight checks, awareness of environmental conditions, and understanding potential hazards are essential for responsible drone operation.
Pre-flight Safety Checklist
A comprehensive checklist ensures all critical aspects are addressed before each flight. This minimizes risks and promotes safe operation.
- Check battery charge level.
- Inspect drone for physical damage.
- Verify GPS signal strength.
- Check weather conditions (wind speed, precipitation).
- Review airspace restrictions and no-fly zones.
- Ensure proper authorization and permits are in place.
- Inform nearby individuals of the drone operation.
Weather Conditions and Airspace Restrictions
Adverse weather conditions, such as strong winds or heavy rain, can severely impact drone stability and control. Similarly, operating within restricted airspace can lead to legal repercussions and safety hazards. Always consult weather forecasts and airspace maps before each flight.
Pre-flight Sequence Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight sequence can aid in a systematic and thorough approach to preparation.
The flowchart would depict a sequence starting with power-on self-tests, moving through battery checks, GPS acquisition, environmental checks (wind, rain, obstructions), and concluding with airspace authorization verification. Each step would branch to a “pass” or “fail” outcome, with “fail” leading to troubleshooting or flight postponement.
Potential Hazards and Mitigation Strategies
Several hazards can arise during drone operation, including collisions with obstacles, loss of signal, and malfunctioning components. Proactive mitigation strategies can significantly reduce these risks.
- Obstacle Avoidance: Utilize visual observation and/or obstacle avoidance systems.
- Signal Loss: Fly within the range of the controller and consider using a range extender.
- Malfunctions: Regularly maintain the drone and have backup batteries available.
Understanding Drone Controls and Navigation
Understanding the drone’s controls and navigation systems is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will explain the function of each control stick and button, demonstrate basic maneuvers, and discuss the use of GPS and other navigational aids.
Drone Remote Control Functions
A typical drone remote features two joysticks, several buttons, and switches. The left joystick generally controls altitude and direction, while the right joystick controls the drone’s pitch, roll, and yaw. Buttons typically activate functions like camera control, return-to-home, and emergency stops.
Basic Drone Maneuvers, How to operate a drone
Mastering basic maneuvers forms the foundation of safe and skillful drone piloting. These include takeoff, landing, hovering, and precise directional control.
- Takeoff: Gently increase throttle until the drone lifts off smoothly.
- Landing: Gradually decrease throttle until the drone gently touches down.
- Hovering: Maintain a stable altitude and position using subtle control adjustments.
- Directional Movement: Use the joysticks to control the drone’s movement in all directions.
GPS and Navigational Aids
GPS is a critical navigational aid for drones, providing precise location information and enabling features like return-to-home and waypoint navigation. Other navigational aids include compass, barometer, and inertial measurement units (IMUs).
Manual vs. Autonomous Flight Modes

Drones typically offer both manual and autonomous flight modes. Manual mode provides direct control over the drone, while autonomous modes allow for pre-programmed flight paths or automated functions like follow-me.
Advanced Drone Maneuvers and Techniques: How To Operate A Drone

Once comfortable with basic maneuvers, pilots can explore more advanced techniques to enhance their flying skills and creative possibilities.
Complex Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers, such as flips, rolls, and 360-degree turns, require practice and precision. These maneuvers are generally only performed in open areas away from obstacles and people.
Waypoint Navigation
Waypoint navigation allows pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously. This is particularly useful for complex shots or aerial surveys.
Achieving Smooth and Stable Footage
Smooth and stable footage is essential for high-quality drone photography and videography. This requires careful control inputs, appropriate flight speeds, and potentially the use of image stabilization features.
Common Flight Errors and Solutions
Understanding common flight errors and their solutions is crucial for safe and efficient drone operation.
- Drift: Caused by wind or GPS signal interference. Solution: Adjust control inputs to compensate or find a more sheltered location.
- Sudden Drops: May be due to low battery or motor failure. Solution: Land immediately and address the underlying issue.
- Unresponsive Controls: Could indicate a connection problem or software glitch. Solution: Check connections, restart the drone, and potentially update firmware.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and prompt troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the longevity and safe operation of your drone. This section provides guidance on cleaning, maintenance schedules, and addressing common malfunctions.
Drone Component Cleaning and Maintenance
Regular cleaning and maintenance of drone components are essential for optimal performance and preventing malfunctions. This includes cleaning propellers, sensors, and the drone body.
- Propeller Cleaning: Gently wipe propellers with a soft cloth to remove dirt and debris.
- Sensor Cleaning: Carefully clean sensors with a soft brush or compressed air.
- Body Cleaning: Wipe the drone body with a damp cloth.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Several malfunctions can occur, often related to battery, GPS, or motor issues. Understanding the causes is crucial for effective troubleshooting.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing common issues promptly can prevent more serious problems and ensure the drone’s continued safe operation.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery or replace it with a fully charged one.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception or restart the drone.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor for damage and replace it if necessary.
Recommended Maintenance Schedule
| Component | Maintenance Frequency | Procedure |
|---|---|---|
| Propellers | After each flight | Inspect for damage; clean with a soft cloth. |
| Battery | Monthly | Check battery health; calibrate if needed. |
| Motors | Every 3 months | Inspect for wear and tear; lubricate if necessary. |
Drone Photography and Videography
Drones offer unique perspectives for capturing stunning aerial photography and videography. This section explains how to optimize camera settings, compose compelling shots, and utilize various flight techniques.
Adjusting Camera Settings for Optimal Image Quality
Optimizing camera settings is crucial for achieving high-quality images and videos. This involves adjusting parameters such as ISO, shutter speed, aperture, and white balance depending on lighting conditions.
Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Composition plays a vital role in creating visually appealing aerial shots. This includes considering the rule of thirds, leading lines, and the overall visual balance of the scene.
Flight Techniques for Specific Footage Types
Different flight techniques are employed to capture specific types of footage. For example, smooth, cinematic shots require slow, controlled movements, while time-lapses require stationary positioning over an extended period.
Effects of Different Camera Angles and Perspectives
A high-angle shot might emphasize the vastness of a landscape, while a low-angle shot could accentuate the scale of a building. A side angle shot might highlight the details of a structure, and a bird’s eye view shot would provide a panoramic perspective.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Operating a drone responsibly involves adhering to all applicable laws and regulations. This section highlights the importance of registration, permits, airspace restrictions, and the legal consequences of non-compliance.
Drone Registration and Permits
Many jurisdictions require drone registration and may necessitate permits for commercial operations or flights in specific areas. It is crucial to check local regulations and obtain the necessary documentation before operating a drone.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, such as pre-flight checks and maneuvering techniques, is crucial. For a comprehensive guide covering everything from takeoff to landing, check out this excellent resource on how to operate a drone and become proficient in piloting your drone safely and effectively.
Remember, responsible drone operation is key to enjoying this exciting technology.
Airspace Restrictions and No-Fly Zones
Airspace restrictions and no-fly zones are implemented for safety and security reasons. These zones often include airports, military bases, and sensitive infrastructure. Operating a drone within these areas is strictly prohibited.
Legal Consequences of Violating Drone Regulations
Violating drone regulations can lead to fines, license suspension, or even criminal charges depending on the severity of the violation. Understanding and adhering to the law is paramount.
Key Legal Considerations for Drone Operation
- Register your drone with the appropriate authorities.
- Obtain necessary permits for commercial operations.
- Always check for airspace restrictions and no-fly zones before each flight.
- Maintain awareness of privacy laws and regulations.
- Operate your drone responsibly and safely.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical understanding and practical application. This guide has provided a foundational framework, covering essential pre-flight procedures, control mechanisms, advanced maneuvers, and legal compliance. Remember that continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and responsible drone pilot. By adhering to best practices and staying informed about evolving regulations, you can unlock the full potential of your drone while ensuring the safety and enjoyment of everyone involved.
Questions Often Asked
What is the minimum age requirement to operate a drone?
Age requirements vary depending on the country and drone classification. Check your local regulations for specific details.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
How far can I fly my drone?
The maximum distance depends on the drone’s capabilities, battery life, and local regulations. Always stay within visual line of sight unless operating under specific exemptions.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
Attempt to regain control using the emergency landing feature if available. If unsuccessful, immediately report the incident to relevant authorities.
How do I ensure my drone footage is legally compliant?
Ensure you are operating within permitted airspace, respecting privacy laws, and obtaining necessary permissions for filming in restricted areas.
